SAP Unique Functionalities for Industry Solution - Mill Products
 Class and Characteristics
Class and Characteristics
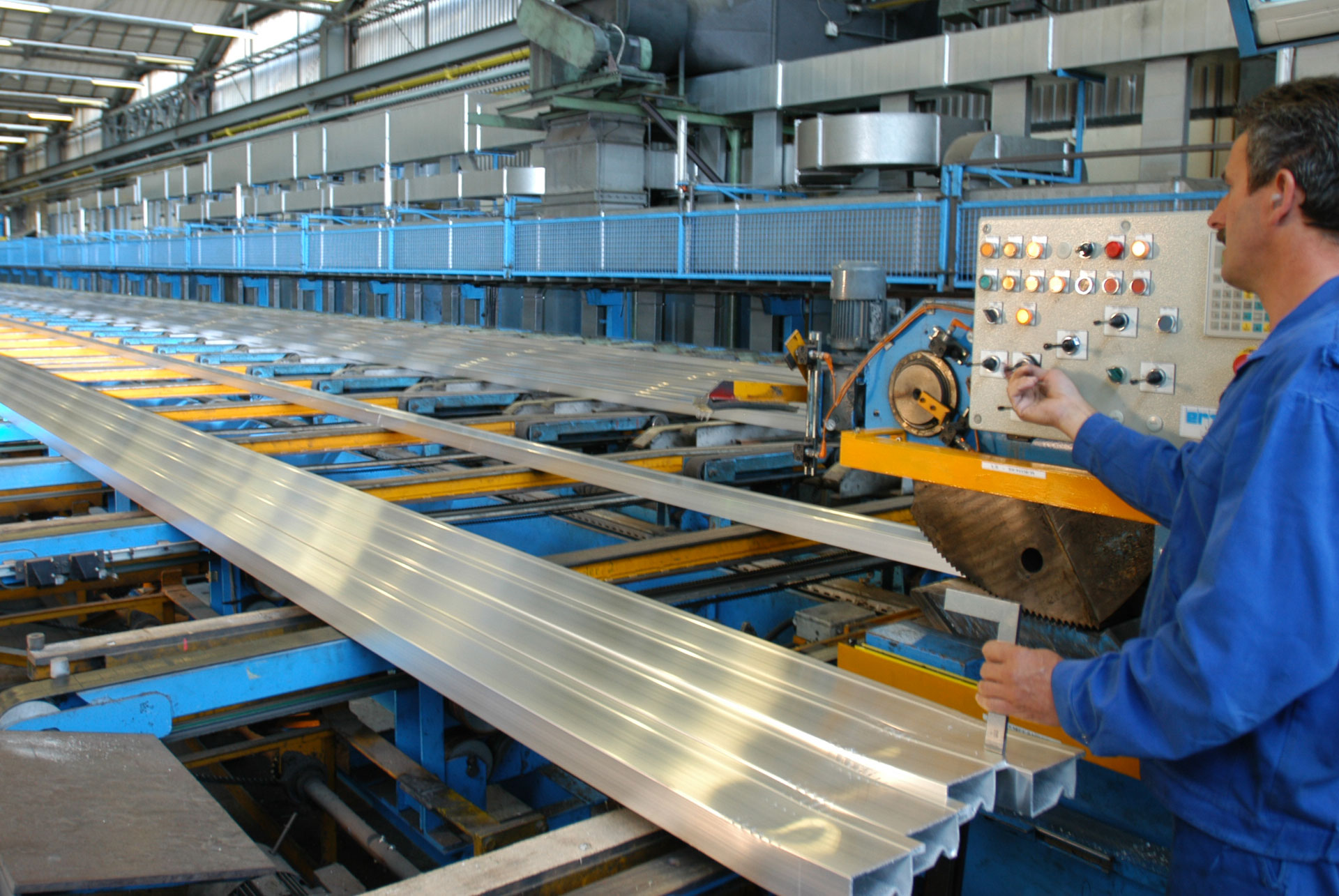
The different branches of the mill industry have in common that they work with a very large number of characteristics and material variants. In addition, the materials used in the previously mentioned industries are primarily oriented toward areas (for instance, paper, cloth, or films) or toward lengths (for instance, cables or pipes). The material properties, described by means of configuration characteristics, must be considered along the entire supply chain.
Owing to this strong affinity to Variant Configuration, this industry solution required enhancements of the SAP S4 Hana standard, and it provides additional functionality that is useful for variant manufacturers. The original standard functionality is still available and ready for use. In the mill industry, the variant diversity is practically unlimited because typically the dimensions of coils must be modelled as characteristics, for example length, width and size can have virtually any value within the technical limits. It’s almost impossible, and not useful, to model each of these attributes as a fully configured variant.
Configurable material is useful if the material have many combination of attributes that go into a product. It means different permutations and combinations of the attributes for same material. In case we maintain a unique material code for each combination, then we require many material numbers. Configurable material may be used in such a case where the user maintain just one generic product code.
Typically configurable material is used in Made To Order (MTO) environment. However frequently ordered configurations may be planned with a material variant which needs to have a material master record. Thus Material variants may have stock and value.
In variant configuration, a class is used to hold the characteristics that describe a configurable material. By linking the class to the configurable material, we allow the material to be configured using the characteristics of the class.
 Fast Data Entry in Sales Order, Production Order, Purchase Order and Goods Receipt
Fast Data Entry in Sales Order, Production Order, Purchase Order and Goods Receipt
The fast data entry functionality can be used to speed up Sales Orders, Goods Receipt and Purchase Orders creation when using Configurable materials or Material Variants. Fast Data Entry functionality enables characteristic value assignments to be entered, within the Sales Order initial screen. Fast Data Entry functionality, a special screen allows to easily enter the characteristic value during Purchase Order and Goods Receipt creation.
In the past the user, always had to go to the characteristic value assignment screen in order to assign values to the characteristics of a material or batch.
This function lets the user enter item data and characteristic values in a single screen. This allows the user to enter items much more efficiently, particularly items with preconfigured materials or material variants for which only a small number of characteristic values need to be assigned.
 Batch Information Cockpit
Batch Information Cockpit
Batch information cockpit ("BIC" - transaction BMBC) is used to search for inventory by attribute (e.g. individual length > 50 m) and display batches and batch inventory with length (and other characteristics).
BIC is batch information cockpit report provides data by plant ,material and batches This report also provides data for all batch classification and changes. The BMBC transaction also provides the user with batch tractability. The Batch information Cockpit (BIC) is a transaction that combines views and analysis of batch information in a single location.
BIC allows the user to select batches, display all the information regarding the batch, access follow-up transactions and use the batch worklists.
 Original Batch
Original Batch
The user can use an original batch to store the original attributes (characteristics) of a production lot or procurement lot, by creating the batch directly for a production order item or a purchase order item. The user can use original batches to store those attributes of a material that do not change throughout the production process.. Using Derivation for Batch Data , the user can also pass on the characteristics from original batches to inventory-managed batches. Original batches are connected to the Batch Where-Used List and the Batch Information Cockpit .
 Combined Production Order Processing
Combined Production Order Processing
In certain segments of industry, including the steel, paper, textile, tools and special-purpose machinery sectors, the same operations are used to manufacture different products. These operations may include producing a melt, continuous casting, and hot and cold rolling. The operations before and after these identical operations are different for different products.
The order combination function allows the user to combine the sequences of identical operations in a consolidated production order. However, there is no system restriction in regard to the combination of production orders with different header material or the mix of MTO and MTS orders.
Purpose:
Combined order is created from two individual orders using the same operations and components.
The confirmation and the goods issue are performed against the combined order.
The goods receipt is performed against the individual orders.
The costs of the combined order are settled to the individual orders
Combining machine processes for orders that run at the same time i.e. Reduction in setup time
Settling the costs to the individual orders.
Benefits:
 Customer Information Record
Customer Information Record
This function lets the user classify a material in the customer-material info record and use it to define a material variant at customer/material level.
The characteristic value assignments that the user enter using this function can be passed on to sales document items by the system. The user can pass on the characteristic value assignments from the customer-material info record to all sales documents.
The material for which the user want to create a customer-material info record must be configurable.
The class and characteristics the user want to use for classification of the customer material info record must be permitted for class type 052 (Material-customer info record) .
 Purchase Information Record
Purchase Information Record
This function lets the user classify a material in the purchasing info record and use it to define a material variant at vendor/material level. The user can pass on characteristic value assignments from the purchasing info record to items of purchase requisitions and purchase orders.
The material that the user want to classify in the purchasing info record must be configurable.
The class and characteristics the user want to use for classification of the purchasing info record must be permitted for class type 057.
The user can classify a material in the purchasing info record at vendor/material level. A different classification at the level of the purchasing organization, plant or info record type is not possible.
When the user create a purchase requisition or purchasing document item for the material, the characteristic values in the purchasing info record can be adopted and if necessary, changed.
 Product Unit and Single Unit Batch
Product Unit and Single Unit Batch
Batches whose stock in piece units of measure can only ever be zero or one .
In certain industry sectors it is necessary to identify materials or means of transportation using a unique number per piece. The user can supply piece numbers for roll cores in the foil industry, paper rolls in the paper industry, and individual cable lengths in the cable industry. The user can map these item numbers as single-unit batches. There is then only one roll or piece per batch.
During the various business processes (for example, during the cutting operation), there may be changes to the quantity of the single-unit batch for these materials. These changes in quantity, however, only affect uncountable units of measure (such as meter, square meter, kilogram); the quantity in "piece" is always either zero or one. The use of single-unit batches, helps the user to ensure that a roll, which always represents one piece, is not inadvertently split into a number of batches; e.g. during stock transfer or partial withdrawals from the paper roll. This enables the user to ensure that a roll is always a unique batch.
A single-unit batch differs from other batches in as far as the Single-Unit Batch indicator is set in the relevant batch master.
 Batch Determination and Quantity Proposal
Batch Determination and Quantity Proposal
Batch Determination is used in inventory management, production, sales and distribution, warehouse management. It is used to select batches and allocate the same in a manufacturing order or in an outbound delivery or in a goods issue/goods transfer in inventory management.
Batch Determination in Outbound Delivery is done within Batch Split functionality through Batch Search Strategy, Selection Class and Sort Rule. There are SAP standard IS-Mill specific Batch determination routine in Delivery for Quantity proposal.
The quantity is fulfilled from first available open batch quantity from the top of the list of batches displayed. In case of partial fulfilment, then the remaining requirement quantity shall move to the next available open quantity and this shall continue until the balance open quantity is exhausted. The batches can also be sorted based on date of manufacture or date of goods receipt.
 Delivery Related Trading Unit Change (DTUC) and Mill Cut Process
Delivery Related Trading Unit Change (DTUC) and Mill Cut Process
IS-Mill user can use the delivery-related trading unit change (DTUC) to change the trading unit of a batch in accordance with the sales order configuration while an outbound delivery is being processed. User can also use it to adjust the characteristic values to suit the customer’s requirements.
IS-Mill can perform all required activities in DTUC, such as changing the characteristic values, distributing the quantity of the issuing batch to new batches, and processing remaining quantities.
The system transfers the DTUC-relevant characteristics from the configuration of the sales order or the stock transport order to the classification of the receiving item and documents all changes in the inventory management material document, which the system generates to enable the tracing of batches.
DTUC invokes the MILL_CUT transaction. The IS-Mill user work with materials managed in batches, it will often be the case that they do not need to use the whole batch at once, but only part of it for a sales order. The rest remains in stock.
Reposting in MILL_CUT enables an issuing quantity is distributed to several receiver quantities. IS-Mill user, can repost batch stock to Residual posting . Residual posting can be to Scrap or Scrap Material or to Stock difference.
 Global and Local Items in Sales Orders and Purchase Orders
Global and Local Items in Sales Orders and Purchase Orders
Sales documents and Purchase Orders have several items that differ only in a few characteristics. Although most characteristic value assignments for the various items are identical, it is generally necessary to assign values to all characteristics separately.
This is a very effective fast and accurate user entry tool.
Now characteristic value assignments can be inherited within a sales document by means of local and global items.
The IS-Mill user can change the characteristic value assignment of a global item, the system shall automatically inherit the changed values to the local items of the global item.
 Non-Ferrous Metal Pricing
Non-Ferrous Metal Pricing
Non-ferrous metal processing (referred to below as NF processing) is concerned with the special features of non-ferrous metals (NF metals) in pricing.
When some products are priced (e.g. aluminum, copper cable), problems may arise because the prices of individual components, such as copper, aluminum fluctuate wildly. Such components are traded on stock/metal exchanges. The current market rates are stored in the system. The logistic processes are designed to enable the system to react to price fluctuations.
NF processing also includes special types of pricing such as coverage (bulk agreements) and provision of material by customers in Sales and Distribution and in Purchasing. In NF metal processing, the IS-Mill user can take account of various pricing arrangements and settlement methods, such as coverage and the provision of materials or components. The system controls the selected settlement method using the rate determination key. Various rate determination routines are used in price determination.
 Reel Calculation
Reel Calculation
Majority of the Cable customer, use the reel calculation to determine the correct reel for a length of material.
The reel calculation determines the optimal combination of cable length and reel. The combination is optimal when the reel can accommodate the cable length without causing damage. If the reel is too small or too large, the cable (and the reel) could be damaged. The system determines not only the optimal reel for a specific cable length but also the smallest possible reel, because this is usually the least expensive.
The reel calculation finds the matching reel for a cable based on the reel parameters (inner width, outer diameter, core diameter, load capacity), the cable parameters (length, cable diameter, cable weight, bending factor), and various Customizing settings for the Reel Calculation.
The customer can have alternative reel determination, where the system ignores the geometry of the reel. Using value tables (Variant table), the IS-Mill system can assign various cable length intervals to reels directly.
 Handling Unit Management
Handling Unit Management
Handling Unit Management (HUM) enables the IS-Mill customer to automatically post packaging materials in an outbound delivery. The material to be packed, the packaging material and any auxiliary packaging materials are mapped as a single handling unit (HU) and are posted together under a single identification number on goods issue.
The cable/ Hot Roll metal Coil must have been physically wound onto the reel/core/drum/bobbin and the material number of the packaging material must have been saved in the batch characteristic before the handling unit is generated.
This function is implemented based on the HUM packing function of the SAP standard system.
Packaging materials that are used to create handling units must have a material master and be suitable for inventory management. The stock is reduced accordingly when a goods issue is posted for the delivery.
Since handling units are nestable, the IS-Mill user can, for example, map the wrapped reels as HU at the lowest level. They can also pack wound reels/coils/rolls/drums/bobbin for delivery in other handling units by using additional packaging materials (for example, pallets and containers), and auxiliary packaging materials.
 Mill Products and Non-Ferrous Metal Specific Packages
Mill Products and Non-Ferrous Metal Specific Packages
SAP have provided within S/4 Hana, standard Mill Products and Non-ferrous relevant specific packages, which are designed to help developers encapsulate, modularize, decouple units in the SAP System. Package consists of Business Objects, Dictionary Objects, Class Library, Programs, Function Group, Includes, transactions, Message class, Area menu, Switch Framework objects and Enhancements.
SAP Mill Product package is “/SAPMP/* “and SAP Non-Ferrous Metal package is “/NFM/*”. The Mill product and Non-ferrous Metal customers can customize their business requirements within these permitted packages.
 Mill Product Finished Goods Production Planning (PP) and Detailed Scheduling (DS) with S4 Hana
Mill Product Finished Goods Production Planning (PP) and Detailed Scheduling (DS) with S4 Hana
PP-DS supports certain industry-specific functions such as order combinations where multiple orders going through the same operation can be combined, and a new order is created to simplify and optimize the planning and execution processes. Mill products (DIMP) are part of the SAP S/4HANA core, PP-DS can be used to leverage the industry functions in SAP S/4HANA, which can be further optimized using PP-DS planning and scheduling functions.
SAP PP-DS on S4 Hana can perform Characteristics Dependent Planning (CDP), it is possible to drive planning dependent components with the same characteristics’ values are netted against the demand elements that have characteristics values assigned to them.
PP-DS CDP makes it possible, to ensure that characteristics matching is possible, to make sure the characteristics matching is executed during planning, and new receipt elements are created to fulfil the demand of the requirement elements with characteristics if there are no existing receipts with the same characteristics value available to fulfil the demand.